Monthly Healthcare Industry Financial Benchmarks
December’s Hospital, Patient Volumes, and Physician Practice Financial Performance


This report highlights the latest trends in financial performance for U.S. hospitals and physician groups, drawn from monthly data from more than 135,000 physicians and over 1,900 hospitals.
U.S. hospitals and health systems endured persistent and growing expense increases throughout 2025 that dampened margin growth despite revenue gains. Highlights from the December 2025 data include:
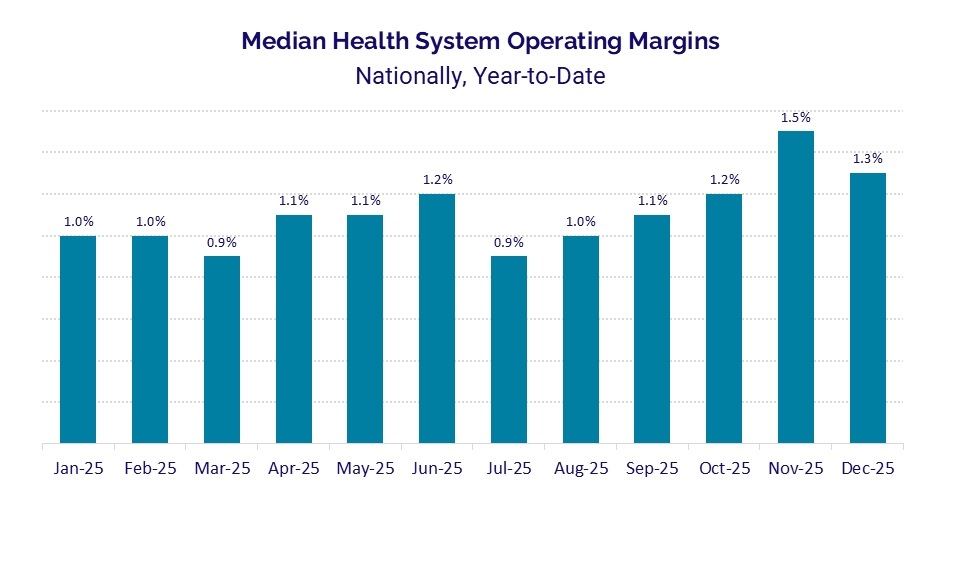
Median health system operating margins declined to 1.3% in December, down from a high of 1.5% in November, after four straight months of improvement.
Supply expenses grew faster than other expense categories to end the year, as hospitals saw non-labor expense increases outpace labor expense growth each month throughout 2025.
Hospital revenues strengthened in December, with gross operating revenue up 11.1% year over year, supported by double-digit growth in outpatient revenue and solid inpatient revenue gains.
Patient volumes were mixed across care settings, as outpatient visits increased 7.2% year over year and inpatient admissions rose 4.2%, while emergency department visits declined and observation volumes remained flat.
Physician practice financial pressures persisted, with the level of investment needed to support operations exceeding $343,000 and per-physician expenses rising to $1.2 million in Q4 2025.
The latest benchmarks illustrate the interplay of revenues and expenses on historically tight hospital operating margins.
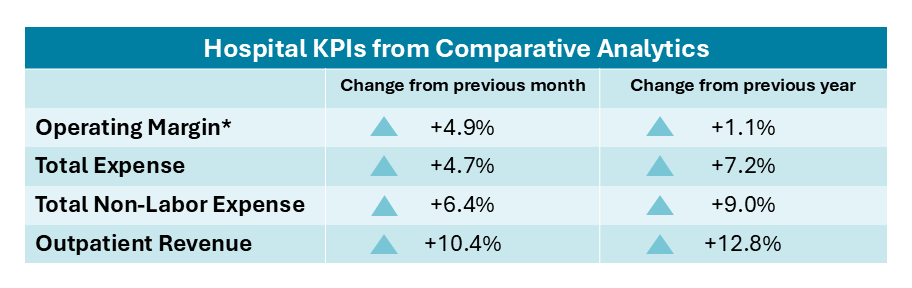
Operating Margins: Health systems across the country saw operating margins take a downturn to close the year in December after four consecutive months of margin growth. The median year-to-date health system operating margin dropped to 1.3% in December, down from 1.5% in November, its highest level of the year. Overall, margins showed limited movement throughout 2025, hovering within two-tenths of a percentage point of 1% for much of the year. While health systems benefitted from greater margin stability compared to recent years, the metric remained thin, reflecting the persistent strain of rising expenses.
At the individual hospital level, however, operating margins saw gains in December. The median change in hospital operating margin increased 1.1 percentage points from December 2024 to December 2025 and rose sharply, by 4.9 percentage points, from November to December. Median operating earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) margin also increased, up 0.7 percentage point YOY and 4.4 percentage points month over month.
Hospital operating margin performance varied by region. While most regions experienced modest changes, hospitals in the Northeast saw a substantial YOY increase of 5.8 percentage points. This compares with median change in operating margin increases of just 0.2 percentage point for hospitals in both the West and Midwest and 0.4 percentage point for those in the South.
Differences by hospital size were more pronounced. Most hospitals posted gains, ranging from a 0.5 percentage point increase for hospitals with 100-199 beds to a 2.5 percentage point increase for those with 300-499 beds. In contrast, the largest hospitals with more than 500 beds reported no change in median operating margin YOY, while the smallest hospitals with 0-25 beds saw margins decline 2.1 percentage points YOY.
Hospital Expenses: Overall hospital expenses continued to rise in December, as they did throughout 2025. Non-labor expenses continued to outpace labor costs, with total non-labor expense up 9.0% YOY and 6.4% month over month. In comparison, total labor expense increased 4.2% YOY and 2.1% from November to December. Total expense increased 7.2% YOY and 4.7% month over month in December. All three metrics saw YOY increases each month of 2025. Total non-labor expense consistently outpaced labor expense growth, with increases ranging from a high of 11.9% YOY in January to a low of 5.1% YOY in May, while total labor expense increases ranged from 8.1% in January to 2.2% in February.
In December, supply expenses posted the largest gains compared to other expense categories. Total supply expense rose 12.3% from December 2024 to December 2025 and 13.5% from November to December 2025. Drug expenses increased 6.1% YOY and 11.1% month over month, and purchased service expense rose 5.1% YOY and 2.3% month over month.
Expense growth was more moderate after adjusting for patient volumes. Total expense per adjusted discharge increased just 0.6% YOY in December and declined 4.1% month over month. Labor expense per adjusted discharge decreased 0.4% YOY and was down 5.3% from November to December. Non-labor expense per adjusted discharge increased slightly, up 0.9% YOY, but declined 2.9% month over month.
Hospital Revenues: Hospital gross revenues increased across all measures in December. Gross operating revenue rose 11.1% YOY, driven by a 12.8% YOY increase in outpatient revenue and a 7.6% YOY increase in inpatient revenue. Revenues also increased month over month in December. From November to December 2025, gross operating revenue increased 10.0%, outpatient revenue rose 10.4%, and inpatient revenue grew 8.7%.
Outpatient revenue growth was consistent across regions, ranging from an 11.2% YOY increase for hospitals in the Midwest to a 14.5% YOY increase for those in the Northeast. Inpatient revenues also increased across all regions, with gains ranging from 6.7% YOY in the West to 11.3% YOY in the Northeast.
Revenue gains were more moderate on a per-patient basis. Net patient service revenue (NPSR) per adjusted discharge increased 1.7% YOY and 2.2% month over month, and NPSR per adjusted patient day rose 4.1% YOY and 3.9% month over month.
While revenue growth was positive for the month, hospitals also experienced increases in uncompensated care. Bed debt and charity care rose 7.0% from December 2024 to December 2025 and was up 1.6% month over month.

Get an in-depth look at current healthcare trends with analyses of financial, operational, and claims data from organizations nationwide, with insights drawn from all of Strata’s datasets.
Hospital inpatient and outpatient volumes are drawn from analysis of more than 10 million patient visits.
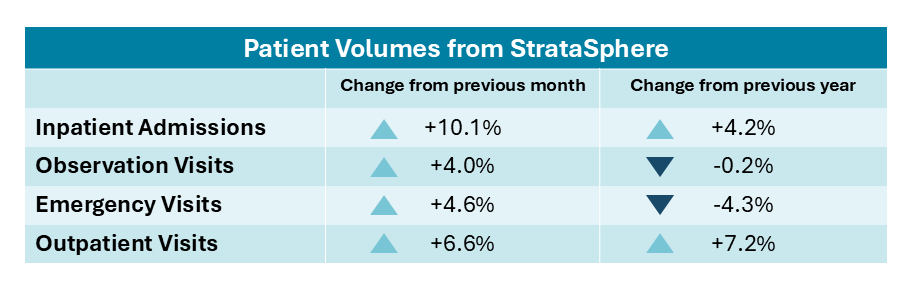
Hospital volumes: Patient demand varied across different care settings in December. Outpatient visits posted the strongest growth, rising 7.2% YOY, while inpatient admissions increased 4.2% over the same period. In contrast, emergency department visits declined 4.3% from December 2024 to December 2025, and observation visits were essentially flat, decreasing just 0.2% YOY.
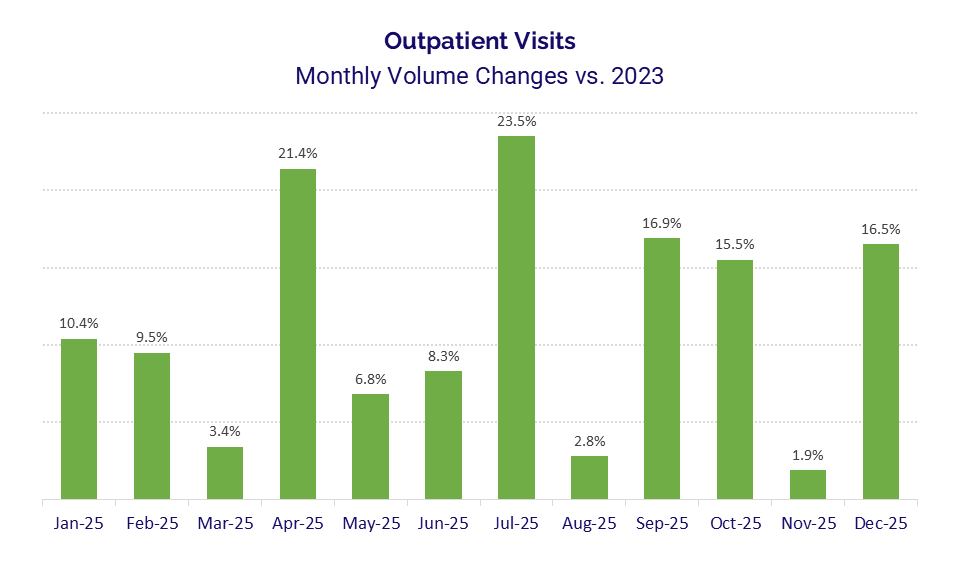
All four metrics increased month over month. Inpatient admissions experienced the largest gain, up 10.0%, followed by outpatient visits at 6.6%, emergency visits at 4.6%, and observation visits at 4.0%. Compared with two years prior, inpatient admissions were up 8.1%, while outpatient visits rose a substantial 16.5% from December 2023 to December 2025.
Regional performance varied. YOY growth in inpatient admissions ranged from 0.4% for hospitals in the West to 6.2% for those in the Northeast. Outpatient visit growth was stronger overall, ranging from 4.1% in the West to 9.2% in the Midwest.
Service line volumes: The latest service line data from November showed varied demand across different specialties. Among those that saw patient volumes grow, ophthalmology experienced the largest YOY increase at 9.4%, followed by rheumatology at 5.4%. Examples of other service lines that experienced YOY increases were: hepatology (4.7%), hematology (3.9%), general surgery (3.1%), cardiology (3.0%), and cancer 2.5%.
Several service lines experienced YOY declines. Normal newborn volumes saw the steepest decrease at 14.3%, followed by infectious disease, which was down 11.6% over the same period.
Procedure volumes: Across 15 common types of procedures, patient volume trends were mixed. The latest data from November show that eight procedures posted YOY increases and seven saw YOY declines. Outpatient upper gastrointestinal endoscopies recorded the largest YOY increase at 10.9%, followed by outpatient positron emission tomography (PET) imaging at 8.8%.
Among procedures that experienced lower demand, YOY decreases ranged from a low of 0.6% for outpatient laboratory disease monitoring screenings to a high of 12.7% for inpatient primary knee replacements.
Children’s hospital volumes: Children’s hospitals experienced mixed patient demand toward the end of the year in December. Inpatient admissions declined 8.4% YOY, while outpatient visits increased 5.7%. Over the same period, observation visits rose 1.8% and emergency visits decreased 10.3%, according to data through December 31.
All four metrics increased from November to December 2025. Inpatient admissions posted the largest gain at 11.5%, followed by observation visits at 6.9%. Emergency visits increased 6.7%, and outpatient visits rose 6.1%.
![]()
A look at last month’s key performance indicators from more than 10,000 physician practices.
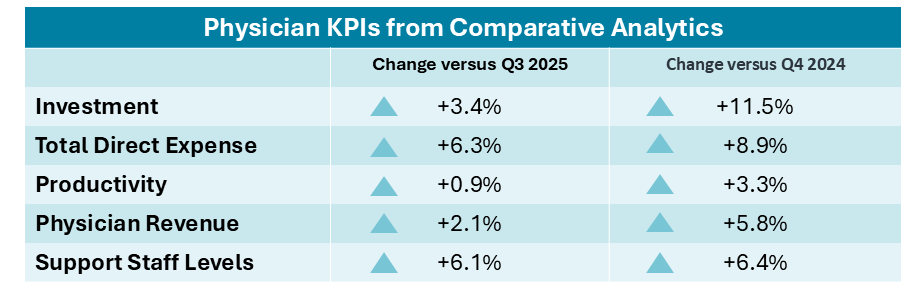
Physician investments: The level of investment required to support physician practice operations continued to increase in the fourth quarter. Median investment per physician full-time equivalent (FTE) rose to $343,128 for the quarter, representing a 3.4% increase compared with the third quarter and an 11.5% increase from Q4 2024.
From Q4 2024 to Q4 2025, investment per physician FTE increased across three of the four census regions. Practices in the South saw a 7.1% increase, those in the West rose 7.3%, and practices in the Northeast experienced a substantial 21.6% increase. In contrast, practices in the Midwest were the only ones to see a decline, with the metric decreasing 9.4% over the same period.
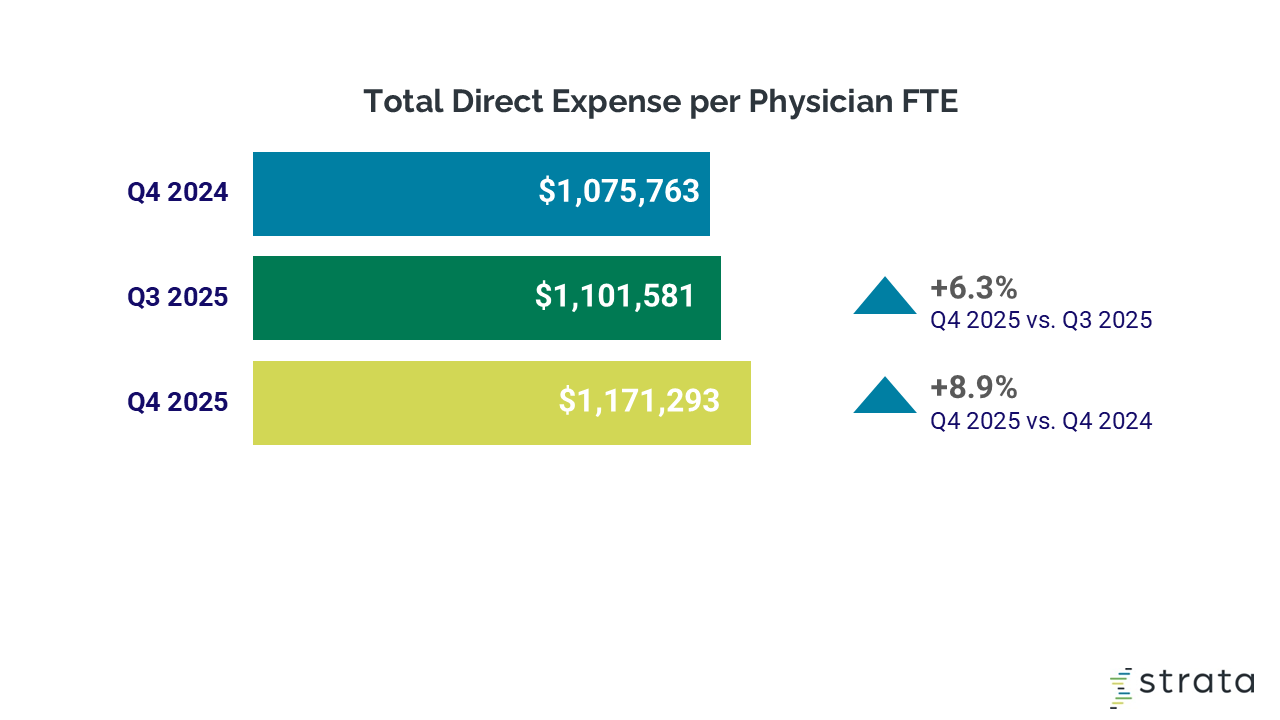
Physician expenses: Physician expenses continued to increase in Q4 2025, contributing to the need for higher levels of physician investment. Total expense per physician FTE reached approximately $1.2 million for the quarter, up 6.3% from the third quarter of 2025 and 8.9% compared with Q4 2024.
These expense pressures were evident across all census regions. Per-physician expenses increased most sharply in the Midwest and Northeast, rising 12.1% and 13.7% from Q4 2024 to Q4 2025, respectively. Practices in the South and West also experienced notable increases, with expenses up 7.4% and 9.6% over the same period.
Physician revenues: Per-physician revenues also remained on the rise in the fourth quarter. Median net patient service revenue (NPSR) per physician FTE rose to $796,816, reflecting a 2.1% increase compared with the third quarter of 2025 and a 5.8% increase from Q4 2024.
NPSR per physician FTE increased across all census regions YOY. Practices in the South saw the largest gain, with revenue up 8.2% from Q4 2024 to Q4 2025. The metric rose 6.6% for practices in both the West and Midwest, and increased 2.7% for practices in the Northeast.
Physician productivity and staffing: Physician productivity showed modest gains in the fourth quarter. Median work relative value units (wRVUs) per physician FTE reached 6,335 in Q4 2025, representing a 0.9% increase compared with Q3 2025 and a 3.3% increase from Q4 2024.
Meanwhile, staffing levels increased at a faster pace over the same period. Median support staff FTEs per 10,000 wRVUs — a measure of staffing levels and productivity — rose to 3.6 for the quarter, reflecting a 6.1% increase from the prior quarter and a 6.4% increase YOY.